Configure the Prometheus Agent
You need to place the examples below in the config section of the agent. Refer to the installation method you used to known which is in your case.
To configure the agent using Helm, you should set up your values.yaml in one of these two ways:
ヒント
You need to add your New Relic in the values.yaml file.
Define which endpoints to scrape
By default, the New Relic Prometheus agent uses two annotations to discover targets: newrelic.io/scrape: "true" and prometheus.io/scrape: "true".
All the targets in the cluster that are annotated with newrelic.io/scrape: "true" are discovered and scraped by default.
The targets annotated with prometheus.io/scrape: "true" will be scraped or not depending on the configuration.
Scrape metrics only from Prometheus integrations
The Prometheus agent can be configured to scrape metrics from the most popular integrations in Kubernetes. Have a look at the list of integrations containing a set of dashboards and to start monitoring out of the box.
That list is defined in the values.yaml of New Relic's Prometheus agent helm chart. You can modify this list, but some might not work out of the box with custom labels or values.
When upgrading, new integration filters might be available. Therefore, the amount of data scraped could increase, depending on the services in your cluster, after an upgrade involving integration filters. You can avoid this by saving a fixed list of app_values in your values.yaml file. For example:
app_values: ["redis", "traefik", "calico", "nginx", "coredns", "kube-dns", "etcd", "cockroachdb"]Moreover, it might happen that a new version of the integrations filters may cause a target that was already scraped by one job to be scraped a second time. In order to receive a notification in the event of duplicated data (and prevent duplicate scraping altogether), you can create an alert based on the following query:
FROM Metric SELECT uniqueCount(job) FACET instance, cluster_name LIMIT 10 SINCE 2 minutes agoIf any value is different from 1 then you have two or more jobs scraping the same instance in the same cluster.
Scrape metrics from all the targets
If you need to scrape all the targets annotated with prometheus.io/scrape: "true", you need to perform one of the following actions, depending on the installation method you chose:
If you used the guided install, select the Scrape all Prometheus endpoints option.
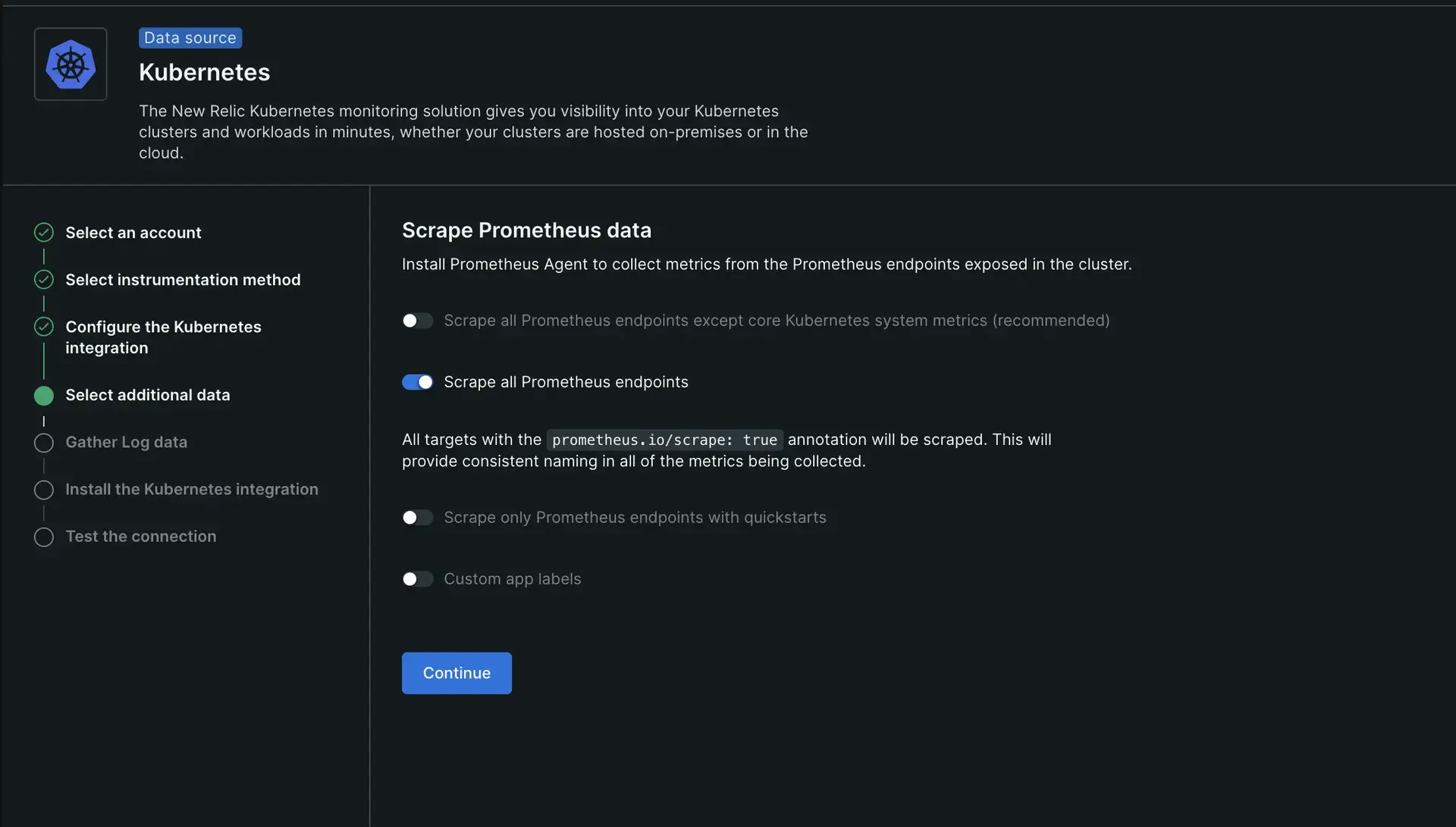
If you used Helm, add the following values in your prometheus-agent configuration:
kubernetes:integrations_filter:enabled: false
Kubernetes target discovery
Kubernetes jobs discover targets and scrape targets according to the target_discovery configuration. If inside the target_discovery configuration, you set pod and endpoints toggles to true, Prometheus will create rules to discover any pod or endpoint in the cluster having an exposed port.
Use the target_discovery.filter configuration parameter to filter in the targets that Prometheus scrapes. Use the label and annotations labels to filter by current conditions, and the AND operator for all conditions.
The following example only scrapes Pods and Endpoints with the newrelic.io/scrape: "true" annotation, and the k8s.io/app label with postgres or mysql as values. For the endpoints, the annotation must be present in the service related to it. The regexes are anchored, that is, if you configure scrape: 'true', Prometheus evaluates true as ^true$. To avoid that, use .*true.* so it also matches a-true-example.
kubernetes: jobs: - job_name_prefix: example integrations_filter: enabled: false target_discovery: pod: true endpoints: true filter: annotations: # <string>: <regex> newrelic.io/scrape: "true" label: # <string>: <regex> k8s.io/app: "(postgres|mysql)"ヒント
If you don't add a value for the label or annotation, the filter will only check if it exists.
Setup static targets
The prometheus agent defines a static target job to scrape self-metrics by default, but you can set up additional static targets by including additional jobs.
This following example includes an additional job to scrape a server managed separately, and the self-metrics job to keep reporting the prometheus agent metrics, as defined by default.
static_targets: jobs: - job_name: managed-exporter targets: - "managed_exporter.your-company.tld:5432" - job_name: self-metrics skip_sharding: true # sharding is skipped to obtain self-metrics from all Prometheus servers. targets: - "localhost:9090" extra_metric_relabel_config: - source_labels: [__name__] action: keep regex: "\ prometheus_agent_active_series|\ prometheus_target_interval_length_seconds|\ prometheus_target_scrape_pool_targets|\ prometheus_remote_storage_samples_pending|\ prometheus_remote_storage_samples_in_total|\ prometheus_remote_storage_samples_retried_total|\ prometheus_agent_corruptions_total|\ prometheus_remote_storage_shards|\ prometheus_sd_kubernetes_events_total|\ prometheus_agent_checkpoint_creations_failed_total|\ prometheus_agent_checkpoint_deletions_failed_total|\ prometheus_remote_storage_samples_dropped_total|\ prometheus_remote_storage_samples_failed_total|\ prometheus_sd_kubernetes_http_request_total|\ prometheus_agent_truncate_duration_seconds_sum|\ prometheus_build_info|\ process_resident_memory_bytes|\ process_virtual_memory_bytes|\ process_cpu_seconds_total"注意
If you modify the static_targets section and don't include self-metrics job, the agent metrics aren't reported.
Target scrape interval
By default, the Prometheus agent scrapes all targets for metrics every 30 seconds as defined in common.scrape_interval for all scraping jobs in the configuration. You can change this by using the scrape_interval key in that section.
This example shows two Kubernetes jobs with different scrape intervals:
common: scrape_interval: 30skubernetes: jobs: # this job will use the default scrape_interval defined in common. - job_name_prefix: default-targets-with-30s-interval target_discovery: pod: true filter: annotations: newrelic.io/scrape: "true"
- job_name_prefix: slow-targets-with-60s-interval scrape_interval: 60s target_discovery: pod: true filter: annotations: newrelic.io/scrape_slow: "true"Metric and label transformations
You can apply metric and label transformations at any configuration section, but setting it at remote write level makes the filtering or transformations wider.
If you set them at newrelic_remote_write level, the filters apply to all metrics that are being sent to New Relic. If you set them at any other section, they apply to the metrics scraped by that section. The metric filter process happens after the metrics have been scraped from the targets.
You can use the extra_metric_relabel_config parameter to apply the filters, which adds entries of the metric_relabel_config parameter. This parameter is present at static_targets.jobs, kubernetes.jobs, and the extra_write_relabel_configs parameter for newrelic_remote_write.
Here's an example of how to use it in different parts of the YAML configuration file:
static_targets: - name: self-metrics urls: - "http://static-service:8181" extra_metric_relabel_config: # Drop metrics with prefix 'go_' for this target. - source_labels: [__name__] regex: "go_.+" action: drop
newrelic_remote_write: extra_write_relabel_configs: # Drop all metrics with the specified name before sent to New Relic. - source_labels: [__name__] regex: "metric_name" action: dropYAML file snippet samples
Add one of these examples in the YAML configuration file from the metric and label transformations section.
To filter metrics
To add or remove metric labels
重要
Metric Labels names must comply with Prometheus DataModel.
Target authorization configuration
Some targets need access authorization to be scraped, like No-SQL Databases to fetch data that the user connecting has access, or exporters that expose sensible data in their metrics endpoint. All authorization methods supported by Prometheus can be configured in the static_targets and kubernetes sections.
As explained in the Installation guide we create a configuration for Prometheus based on our YAML. This part of the configuration passed to Prometheus as-is from our YAML, so you would refer to Prometheus documentation:
- TLS
- OAuth2
- Authorization Header
- Basic Auth
Here are some examples to deal with targets that need access authorization:
kubernetes: jobs: - job_name_prefix: skip-verify-on-https-targets target_discovery: pod: true filter: annotations: newrelic.io/scrape: "true" - job_name_prefix: bearer-token target_discovery: pod: true filter: label: k8s.io/app: my-app-with-token authorization: type: Bearer credentials_file: "/etc/my-app/token"
static_targets: jobs: - job_name: mtls-target scheme: https targets: - "my-mtls-target:8181" tls_config: ca_file: "/etc/my-app/client-ca.crt" cert_file: "/etc/my-app/client.crt" key_file: "/etc/my-app/client.key"
- job_name: basic-auth-target targets: - "my-basic-auth-static:8181" basic_auth: password_file: "/etc/my-app/pass.htpasswd"