With NRQL, you can create queries that group results across time. For example, you can group results together based on timestamps by separating them into buckets that cover a specified range of dates and times.
When using the time functions from the table below in NRQL queries, the results return in UTC. To adjust the results to your time zone, include the WITH TIMEZONE clause in your query.
For the functions that have an optional format parameter, the accepted values are string and numeric. The default format value will be a string if omitted.
Time-based function | Description | String format | Numeric format |
|---|---|---|---|
| Returns the year of a timestamp. |
|
|
| Returns the quarter of the year. The returned value includes both the quarter and the year when formatted as a string. |
|
|
| Returns the month and year of the timestamp when formatted as a string, or the numeric month when formatted as a number. |
|
|
| Returns the week the timestamp occurred by naming the month and day of that week's Monday. |
| N/A |
| Returns the day of the week of the timestamp. The returned value loops back at the end of the week, allowing you to look at trends by weekday over time. |
|
|
| Returns the date of the timestamp. The returned value includes month, day and year. |
| N/A |
| Returns the numeric date within a single month of the timestamp, a value from 1 to 31. The returned value does not include the month. |
|
|
| Returns the number of days in the month of the timestamp. |
|
|
| Returns the hour of the timestamp. The returned value does not include a prepended 0 for hours between 1am and 9am. This differs from functions and clauses such as |
|
|
| Returns the minute of the timestamp. The returned value does not include a prepended 0 for minutes between 1 and 9. This differs from functions and clauses such as |
|
|
Facet your NRQL query time range
Sugerencia
In these examples, we use a custom timestamp attribute submitted with PageView events called createdAt. To facet by the time of PageView event ingestion, you could use the timestamp attribute instead.
To create your NRQL query, use a FACET clause with a bucket function that works with a timestamp attribute. Run a standard FACET query, but instead of faceting by an attribute, facet by time. For example:
SELECT count(*) FROM K8sDaemonsetSample FACET monthOf(createdAt)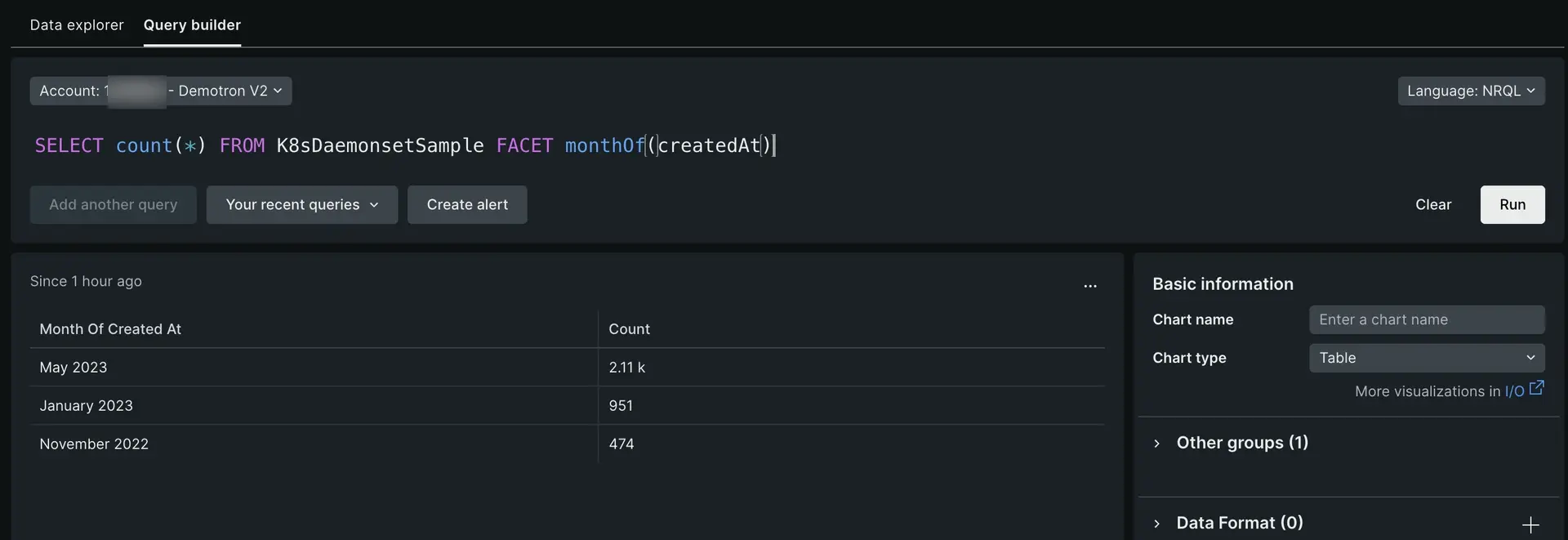
To perform multiple functions within the same query, use NRQL's multi-facet capability:
SELECT count(*) FROM K8sDaemonsetSample FACET dateOf(createdAt), monthOf(createdAt)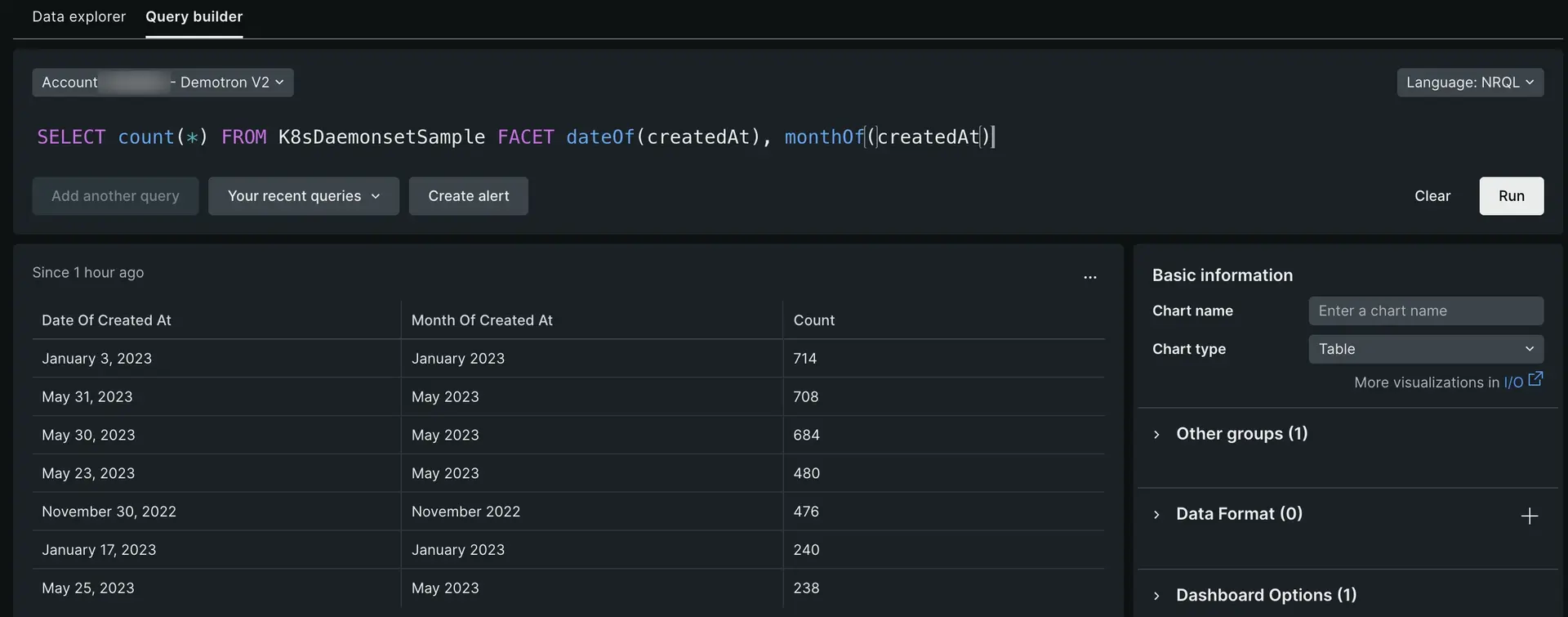
Many time-based functions accept an optional second argument of either string (the default) or numeric, which controls the format of the result value.
SELECT count(*) FROM K8sDaemonsetSample FACET monthOf(createdAt, numeric)